By Ò. Expósito, M. Buchholz, A. Guirado, A. Gallego, M. Mas, P. Riera, D. Luna, S. Laplana,
T. Ruiz, S. Ruiz, M. Gibert, M. Molné*

Abstract
Vytrus leverages more than a decade of expertise in plant regeneration processes to maximize the potential of totipotent plant cell cultures. Within this context, small signaling peptides, known as plant oligopeptides, have been identified for their remarkable wound healing properties and growth factor-like effects. These peptides bear a striking resemblance to animal growth factors and engage in analogous physiological cell processes. Notably, they exhibit a significant growth factor effect on ageing human dermal fibroblasts, offering substantial promise for rejuvenating human skin through mechanisms akin to growth factors. Initial test results suggest that these specific phyto-peptidic fractions possess the capability to reverse the senescence phenotype of ageing fibroblasts, effectively impeding cell ageing and stimulating cell proliferation. These findings present compelling prospects for both cosmetic (anti-ageing) and dermatological (skin regeneration, wound healing) applications, harnessing the potential of natural plant peptides.
Key words: Plant Growth Factors, Totipotent Cells, Plant stem cells, Plant peptides, skin rejuvenation
1. Introduction
In today’s dynamic market landscape, the prominence of oligopeptides is indisputable, with widespread applications in both the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries. Nonetheless, traditional sources for these peptides often rely on human-derived origins, entailing substantial production costs or genetic modifications1,2. Recent examinations have unveiled the remarkable potential of plant-derived oligopeptides, closely mirroring their human counterparts, in instigating the rejuvenation of human skin cells through a growth factor-like effect.
Within the realm of biotechnology, Vytrus Biotech has harnessed its internal expertise to uncover parallels between tissue regeneration processes in plants and animals. This quest led to the identification of a group of small signaling peptides referred to as plant oligopeptides, integral to regeneration and healing mechanisms. Through the pioneering Growth Factor Control development process, Vytrus Biotech has not only successfully identified and produced these plant-derived peptides but also concentrated them, introducing the groundbreaking Phyto-Peptidic Fractions™ (PPF), a patented technology. These PPF originate from an optimized culture of totipotent cells, often referred to as plant stem cells, which possess the remarkable ability to regenerate an entire plant from a single cell3,4,5.
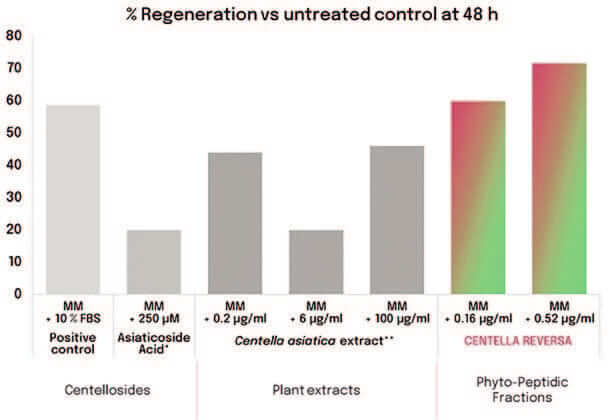
Graph 1. Centella plant peptides regenerative efficacy.6,7
At the core of these totipotent cells’ extraordinary regenerative attributes lies the PPF, positioning them as cutting-edge cosmetic assets adept at preserving the skin’’s innate regenerative potential. Enriched with plant-based growth factors, transcription factors, and epigenetic modulators, these PPF hold immense promise across a wide spectrum of cosmetic and dermatological applications. Their versatile applications encompass stimulating hair growth, combating aging and wrinkles, fostering skin regeneration, expediting wound healing, and beyond.
1.1 Plant-Derived Peptides with Naturally Amplified Effectiveness
Vytrus focused on Phyto-Peptidic fractions of plant stem cells of Centella asiatica, which acts by reversing the skin aging process through its plant growth factors.
Centella Reversa™ is the concentrated secretome of totipotent cells from Centella asiatica. This secretome contains signaling peptides that are designed to reverse the skin aging and have a higher regenerative efficacy compared to traditional range of bioactives from Centella plant extracts or centellosides, which only represent 1–8% of the total plant assets. Therefore, PPF represent a new activity profile for the species: a new range of bioactives (Graph 1).
It is not a surprise that the global peptide skincare market size is greatly growing, expected to reach a valuation from USD 1,069.64 Million in 2022 to worth USD 1,975.43 Million in 2030, according to Global Peptide Skincare Industry Research Report.8 This optimistic forecast may encourage cosmetic companies to develop novelties that tackle the peptide skincare market in ways never imagined.
2. Centella ReversaTM: growth-like factors that revert cell senescence
The Centella plant is known as the longevity plant because of its incredible regenerative and plasticity properties. By using the patented Phyto-Peptidic Fractions platform (PPF), it has been possible to obtain and concentrate the molecules that give the plant these properties.
Centella Reversa™ is a 100% natural active ingredient from Centella asiatica stem cells. This biotechnology active acts with a rejuvenating strategy by reversing cellular senescence, rebuilding the structure of the skin from the inside, and offering an overall improvement of facial complexion, achieving a global rejuvenating effect.
Fig.1. Centella natural peptides: expertise in tissue regeneration
3. Biological activity
A complete panel of studies supports these claims. In vitro tests include wound healing (scratch test) and the study of senescence reversal in Human Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF) within different parameters (cell proliferation, cell detoxification, and DNA protection).
These studies demonstrate that the asset accelerates skin regeneration, delays the effects of aging, activates skin repair and protection processes.
3.1 In vitro wound healing: regenerative properties in HDF
To see the effect of the active, a scratch test was performed, and the healing process was monitored by phase contrast microscopy. Centella Reversa™ accelerated the healing process up to +72% at 48h compared to baseline conditions (Fig. 2). The enhancer effect at 24h was higher than growth medium at 10% (growth medium composition contained benchmark growth factors, used as positive control), showing a Growth Factor-like effect. Non-treated HDF were propagated and grown in growth medium.

Fig.2. Wound healing properties of Centella ReversaTM (in vitro)
3.2 In vitro senescence reversal in Human Dermal Fibroblasts cultures
In order to analyze the effect of the product, on the cellular aging of Human Dermal Fibroblasts (HDF), the expression variation of different senescence markers was evaluated in aged fibroblasts.
To obtain a culture of “senescent HDF”, the primary culture was subcultivated repeatedly in maintenance medium at each time it becomes a confluence of 80–90%, for more than 20 times, by means of routine subcultivation method. These cells were characterized and showed clearly senescent phenotype: morphological and structural changes (increased cell size, change of shape from thin, long, and spindle-like to flattened and irregular, increased membrane rigidity and irregularity, increased number of vacuoles), decreased proliferative index (doubling time > 60h) and β-Gal positive staining.
These in vitro results demonstrated that specific oligopeptide fractions arising from the plant totipotent cell cultures of Centella asiatica have the potential to revert the senescence phenotype of senescent fibroblasts. It has been demonstrated that these oligopeptide fractions have a strong effect reverting the cell senescence processes (such as cell detoxifying or DNA protection) and promoting very efficiently cell proliferation in senescent fibroblasts.
3.2.1 Cell proliferation: β-Galactosidase
Beta-Galactosidase (β-Gal) is a hydrolase specifically over-expressed in senescent cells.9 Centella Reversa™ reduced β-Gal levels up to +41% (Fig. 3). Staining with reagent from commercial kit (X-gal): the blue colour indicates the presence of β-Galactosidase.
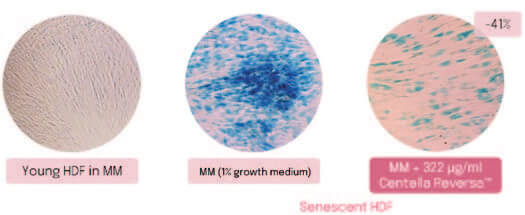
Figure 3. b-Gal positive staining microscopic images of young and aged fibroblasts stained treated with Centella ReversaTM.
3.2.2 Cell detoxification: Peroxiredoxin
Peroxiredoxin-4 (PrxIV) is a peroxidase exerting protection against oxidative stress. Antioxidant enzyme which inactivates ROS10,11. Increased levels of PrxIV in senescent fibroblasts treated with Centella Reversa™ up to 72% were obtained compared to senescent (100%). A dose response effect based on total peptide content is observed (Graph 2).
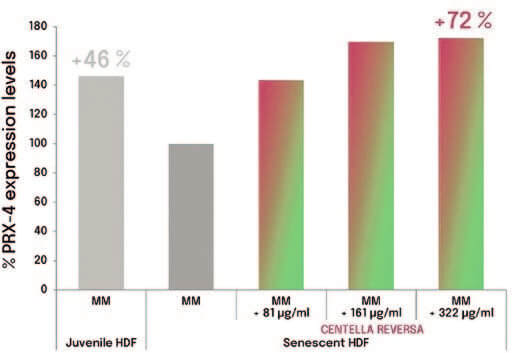
Graph 2. Graph of recovering
detoxification capacity in senescent fibroblasts treated with Centella Reversa™ compared to senescent (100%).
3.2.3 DNA protection: Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1
Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) is a nuclear enzyme responsible for the stability of telomeres. Potentiates DNA repair, protecting telomeres and avoiding their shortening.12,13,14
Increased levels of PARP-1 were obtained in senescent fibroblasts treated with Centella Reversa™ compared to senescent (100%) (Graph 3). A dose response effect based on total peptide content is observed.
Cell morphology: Fibroblast re-shaping
After 8 days incubation with maintenance medium (MM) and + 10 μg/ml Centella Reversa™, reversed morphology of aged fibroblasts to a characteristically younger one was observed. (Fig.4)
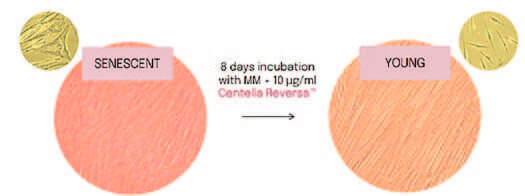
Figure 4. Microscopic images of young and aged fibroblasts treated with Centella Reversa™
4. Clinical evaluation
In vivo tests measure biomechanical properties and wrinkles (firmness and elasticity and clinical evaluation of wrinkle intensity), and facial complexion analysis using VISIA®, showing a holistic rejuvenating effect (wrinkles, texture, pores, visible spots, red areas, porphyrins). These studies demonstrate that the asset rejuvenates skin complexion, achieving a real appearance of 4 years of rejuvenation.
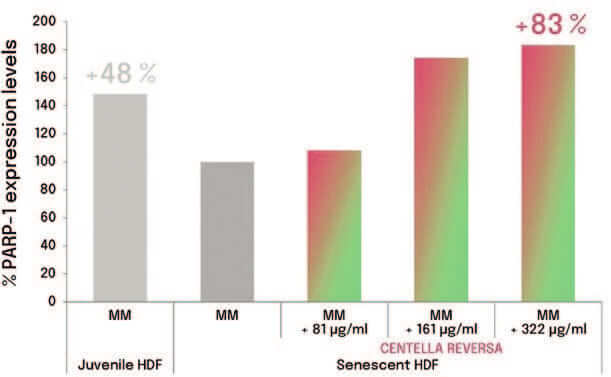
Graph 3: Graph of genomic integrity protection in senescent fibroblasts treated with Centella Reversa™ compared to senescent (100%).
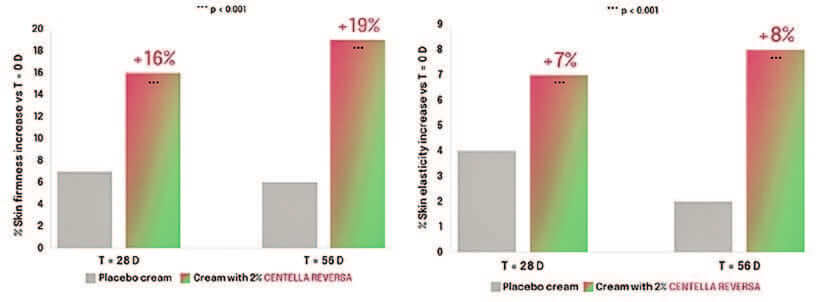
Graph 4. A. Mean values of the parameter Ue reduction obtained with placebo and Centella Reversa™, at 28 and 56 days. A decrease in Ue parameter indicates an increase in skin firmness. B. Mean values of the parameter Ur/Uf increase obtained with placebo and Centella Reversa™, at 28 and 56 days. Increases in Ur/Uf indicate improved elasticity.
4.1 In vivo biomechanical properties and skin wrinkles
Double-blind study vs. placebo was conducted with 20 vol. 51–59-year-old women. 2 applications of Centella Reversa™ at 2% were applied at the crow’s feet. Measurements at 28-56 days were obtained.
Centella Reversa™ significantly increased the skin firmness at 28 and 56 days up to 36% and 46% respectively compared to baseline. Regarding the skin elasticity parameter, Centella Reversa™ significantly increased the skin elasticity at 28 and 56 days by up to 21% compared to baseline (Graph 4). Once calculated the Rejuvenation Index (RI) based in the elasticity parameter and comparing with the reference group of young volunteers (20–25 years), it could be concluded that the older group of volunteers (51–59 years) were:
- 28 days: RI= 12%, equivalent to 3.6 years younger.
- 56 days: RI= 14%, equivalent to 4 years younger.
Regarding the clinical evaluation of intensity of wrinkles, reduced the intensity of wrinkles gradually, being significantly different from the placebo at 56 days with a 9.3% of wrinkle Reduction (WR).
4.2 In vivo and facial complexion analysis
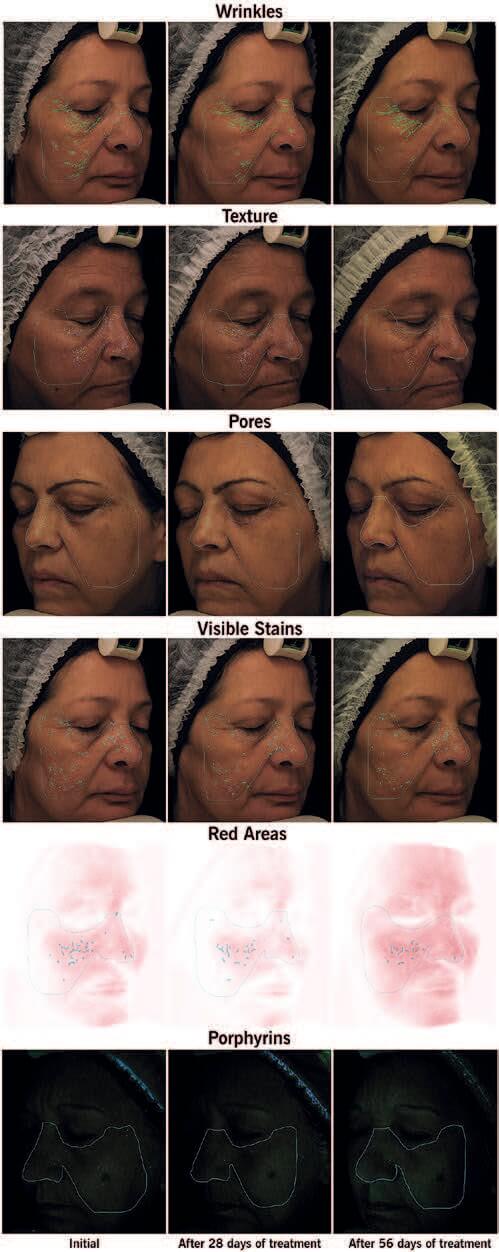
Product’s ability to improve the characteristics of facial skin under three types of lighting was tested. Measurement of 6 different parameters by VISIA® Canfield Imaging Systems: Visible Stains, COSMETICSTexture, Red Areas, Wrinkles, Porphyrins and Pores15. Areas of application: face, measurements at 28–56 days; 2 daily applications by the volunteers (52–63-year-old women) Centella Asiatica Callus Conditioned Media 2%, following the instructions of the study center.
Centella Reversa™ significantly reduced compared to baseline at 28 and 56 days all the parameters (Figure 5):
- Wrinkles, 34% and 40%, respectively.
- Texture, 48% and 53%, respectively.
- Pores, 51% and 57%, respectively.
- Visible stains, 17% and 21%, respectively.
- Red Areas, 45% Areas and 52%, respectively.
- Porphyrins, 68% and 76%, respectively.
5. Conclusion
Considering the compelling evidence from previous findings, it is evident that Genuine Natural Plant Peptides, crafted through an eco-sustainable and readily scalable innovative plant Technology Platform, possess a confirmed growth factor-like effect.
Vytrus has harnessed the power of Centella Reversa™, a 100% natural and COSMOS-approved innovation, to create an active ingredient derived from natural Centella peptides. This breakthrough paves the way for exciting opportunities across cosmetic and dermatological applications, encompassing well-aging, anti-wrinkle treatments, hair growth stimulation, skin regeneration, and wound healing. This distinctive Centella asiatica product offers a multitude of benefits, including firming, anti-sagging, wrinkle reduction, cellular senescence reversal, and telomere protection, establishing it as the pioneering plant-based alternative to animal growth factors.
This scientific breakthrough marks a transformative shift in regenerative peptides and well-aging markets, unveiling a novel discovery within the captivating realm of plant peptides. This emerging category of biotechnology-based active ingredients grants cosmetic formulations new pathways and a diverse range of applications to combat to tackle cellular senescence and enhance the inherent regenerative capabilities of skin through a sustainable solution rooted in plant biotechnology:
- Skin aging treatment and prevention
- Firming, anti-sagging & anti-wrinkles treatments
- Facial treatments, neck, decolleté & hands
- Cica treatments
- Skin imperfections treatments
- Rich nutritive creams and lotions (day & night)
- Natural treatments (serums, gel-creams, creams & masks)
References
- Lo JH, Chen TT. Production of bioactive recombinant human Eb-peptide of pro-IGF-I and identification of binding components from the plasma membrane of human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231). Exp Cell Res. (2018) Jan, 235-243.
- Xiong R, Chen J, Chen J. Secreted expression of human lysozyme in the yeast Pichia pastoris under the direction of the signal peptide from human serum albumin. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (2008) Nov, 129-34.
- Vasil I.K., Vasil V, Redway F. Plant Regeneration from Embryogenic Calli, Cell Suspension Cultures and Protoplasts of Triticum aestivum L. (Wheat). In: Nijkamp H.J.J., Van Der Plas L.H.W., Van Aartrijk J. (eds) Progress in Plant Cellular and Molecular Biology. Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture, (1990) vol 9. Springer, Dordrecht
- Vasil V , Vasil I.K. The Ontogeny of Somatic Embryos of Pennisetum americanum (L.) K. Schum. I. In Cultured Immature Embryos. Botanical Gazette (1982) Dec, 454-465
- Todd J. Jones and Thomas L. Rost, “The Developmental Anatomy and Ultrastructure of Somatic Embryos from Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Scutellum Epithelial Cells, Botanical Gazette 150, no. 1 (1989). Mar, 41-49.
- Korkina LG, Mayer W, de Luca C. Meristem Plant Cells as a Sustainable Source of Redox Actives for Skin Rejuvenation. Biomolecules (2017) May. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5485729/ https://dx.doi.org/10.3390%2Fbiom7020040
- Lee, J-H., Kwon B, H Seo, Park, J-C. H. Asiaticoside enhances normal human skin cell migration, attachment and growth in vitro wound healing model. Phytomedicine (2012), 19: 1223-1227.
- H.A. Azis a, M. Taher a, A.S. Ahmed a, W.M.A.W. Sulaiman b, D. Susanti c, S.R. Chowdhury d, Z.A. Zakaria. In vitro and In vivo wound healing studies of methanolic fraction of Centella asiatica extract. South African Journal of Botany (2017), 108: 163-174.
- Lee, B.Y, A.Han, J., Sub Im, J., Morrone, A., Johung, K., C. Goodwin, E., J. Kleijer, W., DiMaio, D., and Seong Hwang, E. Senescence-associated b-galactosidase is lysosomal b-galactosidase, Aging Cell, 5 (2006) 187-195.
- Han, Y.H., Kim, H.S., Kim, J.M., Kim, S.K., Yu, D.Y., and Moon, E.Y., Inhibitory role of peroxiredoxin II (Prx II) on cellular senescence. FEBS Letters. 579(2005) 4897–4902.
- Bass, J., and Takahashi, S.J., Circadian rhythms: Redox redux, Nature, 27 (2011) 476–478.
- Boesten, D.M.P.H.J., de Vos-Houben, J.M.J., Timmermans, L., den Hartog, G.J.M., Bast, A., and Hagema, G.J., Accelerated Aging during Chronic Oxidative Stress: A Role for PARP-1, Oxid. Med. and Cell. Longev. (2013) Nov. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3844163/ https://dx.doi.org/10.1155%2F2013%2F680414
- Hooten, H.N, Fitzpatrick, M., Kompaniez, K., Jacob, K.D., Moore, B.R., Nagle, J., Barnes, J., Lohani, A., and Evans, M.K., Coordination of DNA repair by NEIL1 & PARP-1: a possible link to aging, Aging, 4 (2012) 674-685.
- Salminen A., A. Helenius, M., Lahtinen, T., and Solovyan, V., Down-Regulation of Ku Autoantigen, DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase, and Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase during Cellular Senescence, Biochem. & Biophys. Res. Com., 238 (1997) 712-716.
- Goldsberry, A., Hanke, C.W., and Hanke, K.E., VISIA system: a possible tool in the cosmetic practice, Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, 13 (2014) 1312-1314.



