According to the European Chemical Agency (ECHA), over 42 kilotons of microplastics end up in the environment each year. Although the environmental harm inflicted by microplastics has been questioned in recent years, there is clear evidence that they accumulate in aquatic life and end up in food and drinking water. A microplastic has been defined by ECHA as a solid or insoluble synthetic polymer with the dimensions smaller than 5 mm This revised definition of microplastics is much broader than the definition that was introduced by ECHA in 2018 and solid microplastic beads were banned in rinse-off cosmetic formulations throughout Europe as a consequence. The revised definition poses a threat to most cosmetic manufacturers as it will include functional synthetic polymers, such as acrylic acid-based polymers, which are used in most cosmetic products today.
Although there are many natural alternatives to these synthetic polymers, they often fall short in terms of properties such as stabilization of suspended ingredients, sensory effects and/or rheological profile.
Fibrillated Cellulose, manufactured by Sappi and branded as Valida, is produced from PEFC-certified, sustainably sourced cellulose. Cellulose is the most abundant natural and biodegradable polymer on earth and the main component of all plants. Unlike conventional cellulose materials, Valida S+ is not chemically modified, nor does it use any chemicals, such as solvents, in its processing. Instead, fibrillated cellulose is fabricated by mechanically processing cellulose fibres into their smallest component, cellulose fibrils, as shown in figure 1. Valida is produced by mechanically treating cellulose fibres to expose their smallest components through a process called fibrillation (figure 1). For this reason, Valida has a naturality of 0.99 according to ISO 16128. Furthermore, it is certified readily biodegradable in marine.

Fibrillated cellulose is an excellent alternative to microplastics as it remains a natural product that provides similar functionalities through the heavily interconnected 3-Dimensional fibre network that is established during the fibrillation process.
The fibre network of Valida, when compared to other natural polymers, provides a significantly larger stabilizing capability. Valida can suspend heavy and lightweight particles in cosmetics formulations, such as UV filters, encapsulated fragrance or oil-in-water droplets. Valida’s shear-thinning rheology profile allows it to do so with a minimal impact on the final viscosity of the formulation.
As such, Valida is an excellent choice for sprayable formulations with a good spray pattern and no dripping after application. As can be seen in figure 2, the Valida network moves when a shear is applied to it, while quickly recovering its structure at rest. The rheology profile introduced by fibrillated cellulose is an important attribute in cosmetics formulations ranging from sprayable products to rich, heavy creams that can be easily spread and offer a quick break.

It should be noted that Valida itself does not give any viscosity to formulations. While this offers interesting formulation possibilities for products requiring stability at low viscosity, it is worth
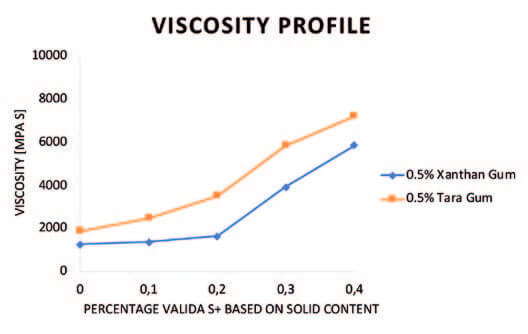
considering the use of a bio-based thickener in conjunction with Valida in viscous formulations. Valida is compatible with rheology modifiers such as Xanthan Gum and Tara gum for use in viscous formulations with various texture profiles. In fact, Valida’s network provides a uniform dispersion to the thickener particles, boosting their efficiency at lower dosages. This synergy is demonstrated in figure 3, where adding Valida S+ (Sappi’s personal care grade) in 0.1% increments to 0.5% of each rheology modifier, significantly boosts the viscosity.
Cellulose is also intrinsically hydrophilic. Valida, with its maintained naturality and large surface area, will therefore offer a refreshing and hydrating skin-feel to formulations. For example, Valida can improve the texture and skin-feel of a sunscreen formulation by creating a lightweight, moisturizing formulation that does not have the tacky or greasy sensory experience one would expect from such a formulation.
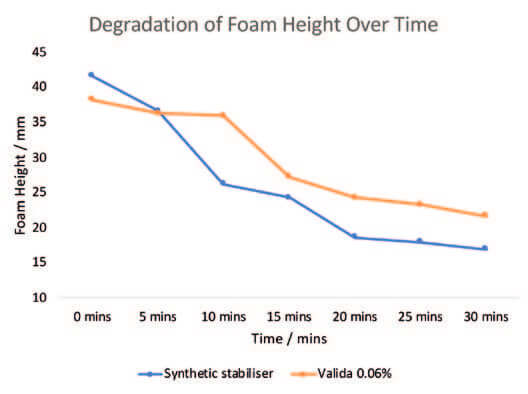
Finally, Valida is extremely tolerant towards electrolytes and a broad range of pH (3–10). As such, Valida can be used in several different cosmetics frameworks, including surfactant systems. Its high yield stress offers a boost to the playtime of foam of mild surfactants, allowing for the creation of creamier foams with improved lathering as demonstrated in figure 4.
In conclusion, Valida’s naturality combined with functionalities such as particle stabilization, thixotropic rheology, skin feel enhancer, foam and SPF boosting make it an excellent alternative to microplastics in personal care formulations. The multifunctional aspects of Valida also lend it for uses beyond the ones described in this article.